CurryTest: A Tool for Testing Curry Programs
CurryTest is a simple tool in the PAKCS and KiCS2 distributions to write and run repeatable unit tests. CurryTest simplifies the task of writing test cases for a module and executing them. The tool is easy to use and comes with a graphical interface that summarizes the results of all tests.
Short Description
In order to define unit tests in a Curry module,
one has to import the system module Assertion.
This module exports an abstract polymorphic type Assertion a
together with the following operations (the first argument
is always a name of the assertion shown in the result of their execution):
assertTrue :: String -> Bool -> Assertion ()
Asserts that an expression has the value True.
assertEqual :: String -> a -> a -> Assertion a
Asserts that two expressions hav equal values.
assertValues :: String -> a -> [a] -> Assertion a
Asserts that an expression (second argument) has a given multiset of values (third argument).
assertSolutions :: String -> (a->Success) -> [a] -> Assertion a
Asserts that a constraint abstraction (second argument) has a given multiset of solutions (third argument).
assertIO :: String -> IO a -> a -> Assertion a
Asserts that an I/O action (second argument) yields a given value (third argument).
assertEqualIO :: String -> IO a -> IO a -> Assertion a
Asserts that two I/O actions yield equal values.
One can define a test program by importing the module
to be tested together with the module Assertion and defining
top-level functions of type Assertion in this module
(which must also be exported).
As an example, consider the following program (TestList.curry)
that can be used to test some list processing functions:
import List
import Assertion
test1 = assertEqual "++" ([1,2]++[3,4]) [1,2,3,4]
test2 = assertTrue "all" (all (<5) [1,2,3,4])
test3 = assertSolutions "prefix" (\x -> x++_ =:= [1,2])
[[],[1],[1,2]]
One can execute a test suite by the command
currytest TestList
Then all exported top-level functions
of type Assertion are tested and the results
are reported together with the name of each assertion.
Thus, we obtain the following successful protocol:
============================================================ Testing module "TestList"... OK: ++ OK: all OK: prefix All tests successfully passed. ============================================================
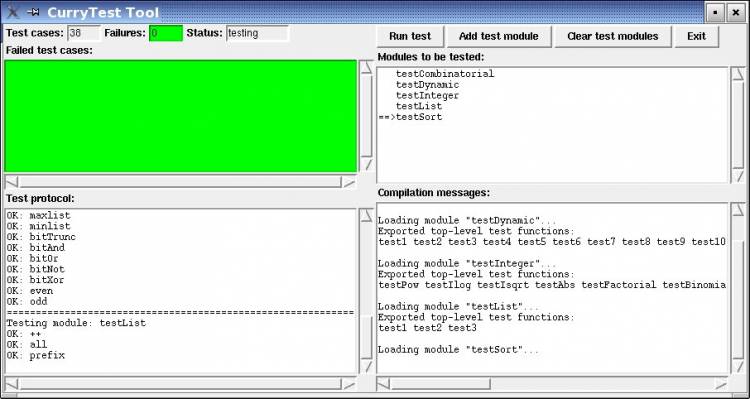
There is also a graphical interface that summarizes the results
more nicely.
In order to start this interface, one has to add the parameter
–window (or -w), e.g., one has to execute a test suite by
currytest --window TestList
A snapshot of the interface is shown below.
More details are described in the user manuals of PAKCS and KiCS2.